The journey of addressing tongue tie issues in children often doesn’t end with the simple procedure of tongue tie release. While the release itself can be a crucial step in improving oral function, it’s equally important to support your child’s oral motor skills as they recover and adapt to their newfound freedom of movement.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the significance of oral motor skills, the impact of tongue tie release on these skills, and strategies for supporting your child’s development post-release.
Understanding Oral Motor Skills
Oral motor skills encompass the coordination and movement of the muscles in and around the mouth, including the lips, tongue, jaw, and cheeks. These skills play a vital role in various functions, such as speaking, eating, swallowing, and even breathing.
For children, the development of strong and coordinated oral motor skills is essential for overall health and well-being.
Impact of Tongue Tie on Oral Motor Skills
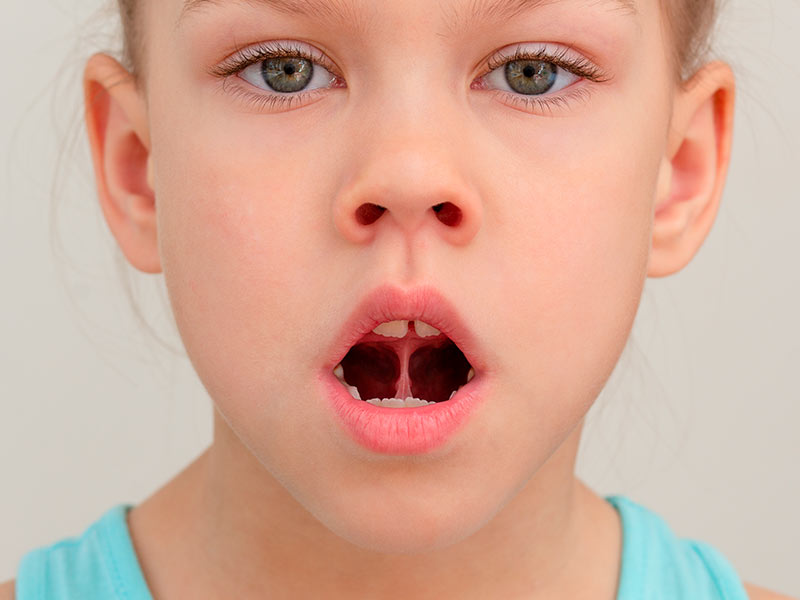
Tongue tie, also known as ankyloglossia, occurs when the tissue connecting the tongue to the floor of the mouth is unusually tight or short, restricting the tongue’s movement.
This restriction can significantly impact a child’s oral motor skills, leading to difficulties with breastfeeding, eating solid foods, articulating speech sounds, and maintaining proper oral hygiene.
After undergoing a tongue tie release procedure, children often experience newfound freedom of movement in their tongues. While this can be a positive development, it also requires support and guidance to help them adapt to their enhanced oral function effectively.
Strategies for Supporting Oral Motor Skills After Tongue Tie Release
Oral Exercises
Your pediatric dentist or healthcare provider may recommend specific oral exercises to help strengthen and coordinate the muscles in your child’s mouth. These exercises may involve tongue movements, lip exercises, and jaw exercises tailored to your child’s needs.
Feeding Therapy
If your child has experienced feeding difficulties due to tongue tie, feeding therapy can be beneficial in helping them develop proper feeding techniques and overcome any challenges they may face. A feeding therapist can provide guidance on positioning, latching, and sucking techniques to support successful feeding.
Speech Therapy
For children experiencing speech delays or articulation difficulties as a result of tongue tie, speech therapy can be instrumental in improving their communication skills. Speech therapists can work with your child to address speech sound errors, improve clarity of speech, and develop proper tongue placement and movement patterns.
Myofunctional Therapy
Myofunctional therapy focuses on correcting improper oral muscle function and swallowing patterns. This type of therapy can be beneficial for children with tongue tie who may have developed compensatory habits or abnormal swallowing patterns. Myofunctional therapists can provide exercises and techniques to retrain the muscles of the mouth and promote optimal oral function.
Consistent Follow-Up
Regular follow-up appointments with your pediatric dentist or healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your child’s progress after tongue tie release. These appointments allow for ongoing assessment of oral motor function, identification of any areas of concern, and adjustments to treatment as needed.
Addressing Tongue Tie
Supporting your child’s oral motor skills after tongue tie release is essential for promoting optimal oral health and function.
By incorporating strategies such as oral exercises, feeding therapy, speech therapy, myofunctional therapy, and consistent follow-up care, you can help your child develop strong and coordinated oral motor skills and overcome any challenges associated with tongue tie.
If you or your child are experiencing symptoms of tongue tie, contact us for personalized recommendations based on your child’s unique needs and circumstances. With the right support and guidance, your child can thrive and enjoy improved oral function for years to come.